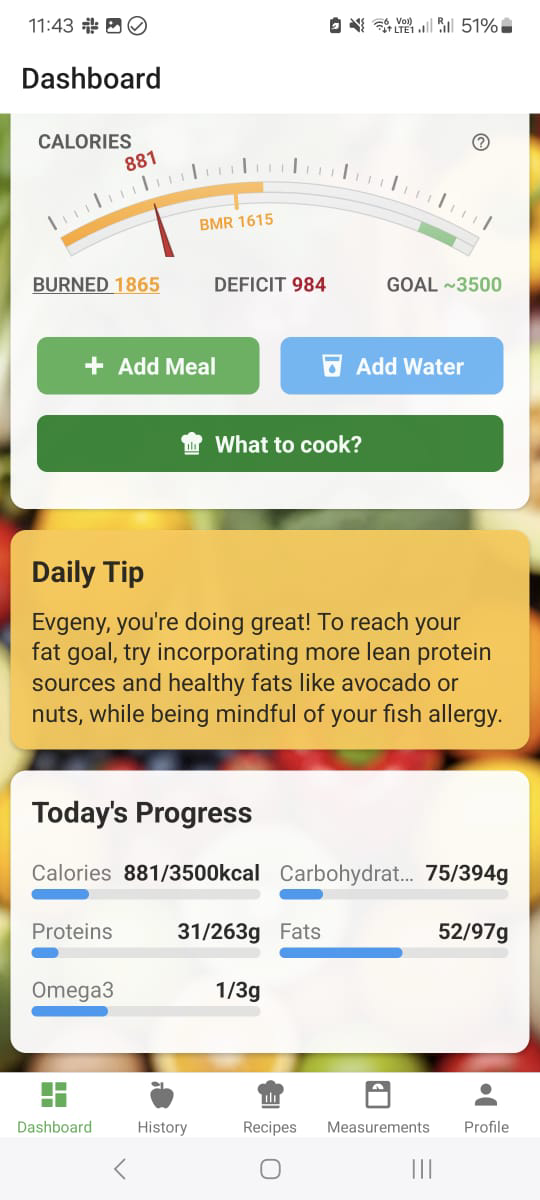
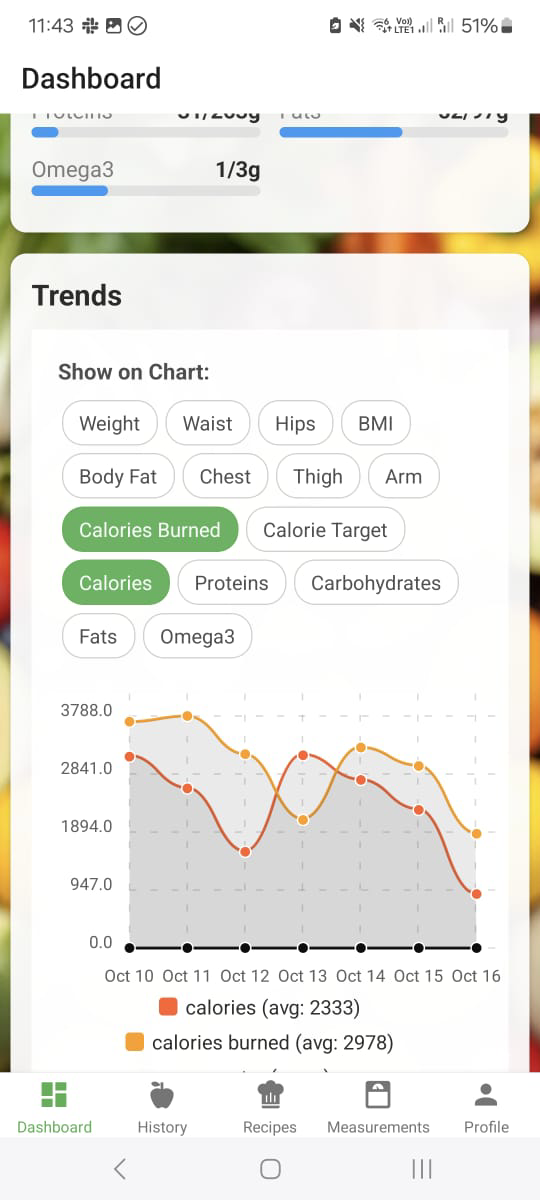
Why Endurance Nutrition Matters
Whether you're training for your first 5K or preparing for an Ironman triathlon, nutrition is the foundation that determines how far and how fast you can go. Poor fueling strategies can lead to hitting the wall, cramping, gastrointestinal distress, and underperformance—no matter how perfect your training plan is.
Endurance athletes face unique nutritional challenges that differ significantly from other sports. Your body can only store about 90-120 minutes worth of glycogen (carbohydrate energy), yet many endurance events last 2-6 hours or more. This means you must master the art of fueling before, during, and after exercise to maintain energy levels and optimize performance.
The Performance Equation
Training + Proper Nutrition + Recovery = Peak Performance
Studies show that proper nutrition can improve endurance performance by 3-5%, which can mean the difference between a personal best and hitting the wall.
Understanding Energy Systems for Endurance
Your body uses three primary energy systems during exercise, and understanding them helps you fuel appropriately:
⚡ Phosphocreatine System
Duration: 0-10 seconds
Fuel Source: Stored ATP and creatine phosphate
Use: Explosive starts, sprints
🔥 Glycolytic System
Duration: 10 seconds - 2 minutes
Fuel Source: Carbohydrates (without oxygen)
Use: High-intensity efforts
🌬️ Aerobic System
Duration: 2+ minutes
Fuel Source: Carbs and fats (with oxygen)
Use: Primary system for endurance
For endurance training, you primarily rely on the aerobic system, which uses both carbohydrates and fats as fuel. At lower intensities (conversational pace), your body can efficiently burn fat. As intensity increases, you shift to burning more carbohydrates because they provide energy more quickly.
The Carbohydrate-Fat Crossover
At low-moderate intensity (50-65% max heart rate), your body burns approximately 50% fat and 50% carbohydrates. As intensity increases toward race pace (75-85% max heart rate), carbohydrate usage increases to 70-80%, which is why carb availability becomes critical for endurance performance.
Daily Training Nutrition: Building Your Foundation
Your daily nutrition habits determine your training quality, recovery speed, and injury resistance. Here's how to structure your baseline nutrition:
Macronutrient Distribution for Endurance Athletes
Carbohydrates
5-12g per kg body weight
Fuels training and replenishes glycogen
Protein
1.2-1.6g per kg body weight
Supports muscle repair and adaptation
Fats
0.8-1.5g per kg body weight
Provides sustained energy and hormonal support

Carbohydrate Periodization
Not all training days require the same carbohydrate intake. Match your carbs to your training load:
🟢 Easy/Recovery Day
3-5g carbs/kg body weight
Lower volume, focus on quality carbs and recovery
🟡 Moderate Training Day
5-7g carbs/kg body weight
Standard training, balanced nutrition
🔴 High-Intensity/Long Day
7-12g carbs/kg body weight
Heavy training load, maximize carb intake
Sample Daily Meal Plan (70kg/154lb athlete, moderate training day)
🌅 Breakfast (7:00 AM)
Oatmeal power bowl:
- 1 cup oatmeal with berries
- 1 tablespoon almond butter
- 1 banana
- Greek yogurt
~650 calories | 100g carbs | 25g protein | 15g fat
🏃 Pre-Workout Snack (9:30 AM)
Quick fuel:
- Rice cake with honey
- Banana
~200 calories | 45g carbs
🥗 Lunch (12:30 PM)
Recovery bowl:
- Grilled chicken breast
- Quinoa (1.5 cups)
- Mixed vegetables
- Avocado half
~700 calories | 85g carbs | 45g protein | 18g fat
🍎 Afternoon Snack (3:30 PM)
Energy boost:
- Apple with peanut butter
- Handful of trail mix
~350 calories | 40g carbs | 12g protein | 18g fat
🍽️ Dinner (7:00 PM)
Power plate:
- Salmon (6 oz)
- Sweet potato (large)
- Roasted vegetables
- Side salad with olive oil
~750 calories | 80g carbs | 50g protein | 25g fat
Daily Total: ~2,650 calories | 350g carbs (5g/kg) | 132g protein (1.9g/kg) | 76g fat
Pre-Workout Fueling Strategy
What you eat before training affects your energy levels, performance, and how well you tolerate nutrition during exercise. Timing is everything.
Pre-Workout Nutrition Timeline
3-4 Hours Before
Full Meal (400-800 calories)
- High carbs: 100-150g
- Moderate protein: 20-30g
- Low fat: 10-15g
- Low fiber to avoid GI issues
Example: Pasta with lean chicken, white bread, banana
1-2 Hours Before
Light Meal (200-400 calories)
- Carb-focused: 50-75g
- Minimal protein: 10-15g
- Minimal fat and fiber
Example: White bagel with honey, banana, sports drink
15-30 Minutes Before
Quick Carbs (100-200 calories)
- Fast-digesting carbs: 25-50g
- No protein or fat
- Liquid or very simple
Example: Energy gel, sports drink, dried fruit
💡 Pro Tip: Practice Your Pre-Race Nutrition
Never try new foods or timing strategies on race day. Use your long training runs to practice your pre-workout fueling routine. What works for one athlete may cause GI distress for another.
Fueling During Exercise: The Performance Window
For workouts lasting longer than 60-90 minutes, consuming carbohydrates during exercise can significantly improve performance and delay fatigue.
Carbohydrate Intake Guidelines by Duration
⏱️ <45 Minutes
No fuel needed
Water sufficient if properly fueled before
⏱️ 45-75 Minutes
Small amounts beneficial
15-30g carbs per hour
Mouth rinse may be effective
⏱️ 1-2.5 Hours
30-60g carbs per hour
Single carb source (glucose, maltodextrin)
Standard sports drinks and gels
⏱️ 2.5+ Hours
60-90g carbs per hour
Multiple carb sources (glucose + fructose)
2:1 ratio glucose to fructose optimal

Fuel Options and How to Use Them
🎯 Train Your Gut
Your gastrointestinal system can be trained to tolerate higher carbohydrate intake during exercise. Start with 30-40g per hour and gradually increase over 4-6 weeks. Studies show trained athletes can absorb up to 90g per hour using multiple carb sources.
Sample Fueling Plan: Marathon (3.5 Hours)
- Mile 6 (45 min): Energy gel + water (25g carbs)
- Mile 10 (1:15): Sports drink at aid station (15g carbs)
- Mile 13 (1:45): Energy gel + water (25g carbs)
- Mile 16 (2:15): Energy chews + water (24g carbs)
- Mile 20 (2:45): Energy gel + water (25g carbs)
- Mile 23 (3:15): Sports drink or gel (20-25g carbs)
Total: ~140g carbs (~40g per hour) + consistent hydration
Post-Workout Recovery Nutrition
The 30-120 minutes after exercise is your most critical window for recovery. Proper post-workout nutrition accelerates glycogen replenishment, reduces muscle damage, and prepares you for your next training session.
The Recovery Window Strategy
🕐 0-30 Minutes: Immediate Recovery
Quick liquid nutrition
- 30-50g fast carbs
- 15-25g protein
- 3:1 or 4:1 carb-to-protein ratio
Example: Chocolate milk, protein shake with banana, recovery drink
🕑 1-2 Hours: Full Recovery Meal
Balanced whole food meal
- 1-1.2g carbs per kg body weight
- 20-40g high-quality protein
- Moderate healthy fats
- Vegetables for antioxidants
Example: Grilled chicken with sweet potato and vegetables, salmon with rice and greens
Optimal Recovery Foods
🍚 Best Carb Sources
- White rice (fast-digesting)
- Potatoes and sweet potatoes
- Oatmeal and cereal
- Bananas and dried fruit
- Pasta and bread
- Sports recovery drinks
🥩 Best Protein Sources
- Whey protein powder (fast)
- Greek yogurt
- Eggs
- Chicken and turkey
- Fish (salmon, tuna)
- Cottage cheese
⚡ Quick Recovery Hack
Chocolate milk is scientifically proven to be one of the most effective recovery drinks, providing the ideal carb-to-protein ratio plus electrolytes and fluid for rehydration. It's convenient, affordable, and tastes great!
Hydration Strategy for Endurance Athletes
Dehydration of just 2% body weight can decrease performance by 10-20%. For endurance athletes, proper hydration is as important as fueling strategy.
Daily Hydration Baseline
Start every day properly hydrated using this formula:
Base fluid needs = 30-40ml per kg body weight per day
For a 70kg (154lb) athlete: 2.1-2.8 liters (70-95 oz) per day
Hydration During Exercise
Before Exercise
2-4 hours before: 5-7ml per kg (350-500ml for 70kg athlete)
15-30 min before: 200-300ml
Check urine color: pale yellow = well hydrated
During Exercise
General guideline: 400-800ml per hour
Hot weather: Increase to 800-1000ml per hour
Sweat rate test: Weigh before/after to determine personal needs
After Exercise
Rehydration formula: 150% of fluid lost
Lost 1kg (2.2lb)? Drink 1.5L over next 2-4 hours
Include sodium to enhance retention
Electrolyte Balance
For exercise lasting longer than 60 minutes or in hot conditions, you need more than just water:
- Sodium: 300-600mg per hour (critical for fluid retention)
- Potassium: 100-200mg per hour (muscle function)
- Magnesium: 20-40mg per hour (prevents cramping)

🧂 Calculate Your Sweat Rate
1. Weigh yourself naked before exercise
2. Train for 1 hour at race pace (don't drink)
3. Weigh yourself again
4. Weight loss in kg × 1000 = ml lost per hour
5. Aim to replace 75-80% during exercise
Carb-Loading Protocol for Race Day
For events lasting longer than 90 minutes, carbohydrate loading can increase glycogen stores by 30-50%, providing extra fuel reserves when you need them most.
Modern 36-Hour Carb-Loading Protocol
The old-school depletion phase is outdated. Modern research shows better results with this approach:
Day 3 Before Race
Normal training taper
Regular nutrition: 5-7g carbs/kg
Light training, start reducing fiber
Day 2 Before Race
Begin loading
8-10g carbs/kg body weight
Very easy exercise or rest
Low fiber, easily digestible carbs
Day 1 Before Race
Peak loading
10-12g carbs/kg body weight
Complete rest
Early dinner, familiar foods only
Race Morning
Top off glycogen
2-4g carbs/kg (3-4 hours before)
Simple, tested breakfast
Follow your practiced routine
Sample Carb-Loading Day (70kg athlete - 700g carbs target)
- Breakfast: White bagel with jam, banana, orange juice (150g carbs)
- Snack: Sports drink, granola bar (60g carbs)
- Lunch: Large pasta with marinara sauce, white bread (180g carbs)
- Snack: Rice cakes with honey, fruit smoothie (80g carbs)
- Dinner: White rice, grilled chicken, white bread (150g carbs)
- Evening snack: Cereal with low-fat milk, banana (80g carbs)
⚠️ Carb-Loading Tips
- Choose low-fiber carbs to prevent GI distress
- Reduce fat and protein slightly to make room for carbs
- You'll gain 2-3 lbs of water weight (this is normal!)
- Only necessary for races 90+ minutes
- Practice during training, not first time on race week
Race Day Nutrition Plan
Race day is when all your nutrition practice comes together. Here's a comprehensive timeline for optimal performance:
Marathon Race Day Timeline
6:00 AM (3 hours before 9:00 AM start)
Pre-race meal
2-4g carbs per kg body weight
Example: 2 bagels with honey, banana, sports drink
8:30 AM (30 min before start)
Final fuel
Energy gel + 200ml water
Use bathroom one last time
During Race
Consistent fueling
30-60g carbs per hour
400-800ml fluid per hour
Start fueling at 45-60 minutes
Finish Line
Immediate recovery
Recovery drink or chocolate milk
Rehydrate with electrolytes
1-2 Hours Post-Race
Recovery meal
Balanced meal with carbs and protein
Continue rehydrating
Race Day Checklist
- ✅ Lay out all nutrition the night before
- ✅ Eat only foods you've tested in training
- ✅ Bring backup gels/chews
- ✅ Know where aid stations are located
- ✅ Set watch alerts for fueling intervals
- ✅ Start hydrating early (don't wait until thirsty)
- ✅ Have a pacing strategy to conserve glycogen early
- ✅ Pin gels to your race bib or shorts for easy access
How Nutrivio Optimizes Your Endurance Nutrition
Managing endurance nutrition can be complex, but Nutrivio makes it simple with AI-powered tracking and personalized guidance.
📊 Precise Macro Tracking
Track your carbohydrate periodization effortlessly. Nutrivio automatically calculates your daily carb needs based on training load, ensuring you're properly fueled for hard training days and recovering on easy days.
🔥 Automatic Calorie Burn Tracking
Connect your Strava account to automatically sync your runs, rides, and workouts. Nutrivio imports your calorie burn data from each activity, giving you a complete picture of your energy expenditure and helping you adjust your nutrition intake accordingly.
📸 AI Food Recognition
Snap a photo of your pre-workout meal or recovery snack, and Nutrivio's AI instantly logs your nutrition. No more tedious manual entry when you're tired from training.
💧 Hydration Tracking
Log your fluid intake throughout the day and during workouts. Nutrivio helps you stay on top of hydration with personalized targets based on your training volume.
📈 Performance Analytics
Correlate your nutrition data with training performance. See how different fueling strategies affect your energy levels, recovery, and workout quality over time.
🚀 Fuel Your Best Performance
Join thousands of endurance athletes using Nutrivio to optimize their nutrition and achieve their racing goals. Download now and get your first two weeks of premium features free!
Common Endurance Nutrition Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Starting Fueling Too Late
Problem: Waiting until you're hungry or tired means you're already depleted.
Solution: Start fueling at 45-60 minutes, even if you feel fine. Prevention is key.
❌ Not Practicing Nutrition
Problem: Trying new gels or foods on race day leads to GI disasters.
Solution: Test all race nutrition during long training sessions. "Nothing new on race day."
❌ Overhydrating
Problem: Drinking too much water without electrolytes can cause hyponatremia.
Solution: Drink to thirst, use electrolytes, know your sweat rate.
❌ Insufficient Carbs on Rest Days
Problem: Cutting carbs on rest days impairs recovery and next-day training.
Solution: Reduce but don't eliminate carbs. You're still recovering and adapting.
❌ Ignoring Post-Workout Nutrition
Problem: Missing the recovery window delays glycogen replenishment and adaptation.
Solution: Have recovery nutrition ready. Even if not hungry, consume liquid nutrition.
❌ Too Much Fiber Pre-Race
Problem: High-fiber foods before racing cause cramping and bathroom emergencies.
Solution: Switch to low-fiber carbs 24-48 hours before race day.
Key Takeaways: Your Endurance Nutrition Action Plan
1️⃣ Build Your Daily Foundation
Match carbohydrate intake to training load (3-12g/kg). Higher carbs on hard training days, moderate on easy days. Consistency matters more than perfection.
2️⃣ Master Your Timing
Fuel 2-4 hours before, 30-60g carbs per hour during long efforts, and recover within 30 minutes post-workout. Timing amplifies the effectiveness of nutrition.
3️⃣ Practice Makes Perfect
Use training to dial in your nutrition strategy. Test different foods, timing, and amounts before race day. Your gut needs training too.
4️⃣ Hydration is Performance
Calculate your sweat rate, use electrolytes for long efforts, and maintain daily hydration baseline. Don't wait until you're thirsty.
5️⃣ Track and Optimize
Use Nutrivio to monitor your nutrition, identify patterns, and continuously improve. Data-driven decisions lead to breakthrough performances.
Endurance performance isn't just about training volume and intensity—it's about providing your body with the right fuel at the right time. Whether you're training for a 10K or an ultra-marathon, proper nutrition is the difference between hitting your goals and hitting the wall.
Start implementing these strategies gradually, track your progress with Nutrivio, and remember: small, consistent improvements in your nutrition will compound into significant performance gains over time.
Now it's time to fuel your best performance. Download Nutrivio today and take control of your endurance nutrition!